Cavitations
Dental foci/ ,,Field of disturbances"
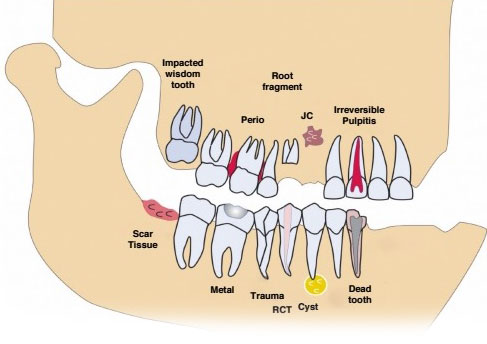
Above shows: Impacted wisdom tooth. Perio. Root fragment. JC. Irreversible Pulpitia. Scar tissue. Metal. Trauma. RCT. Cyst. Dead tooth
2. Jaw Cavitation (JC)
Neuralgia inducing cavitational osteonecrosis (NICO)
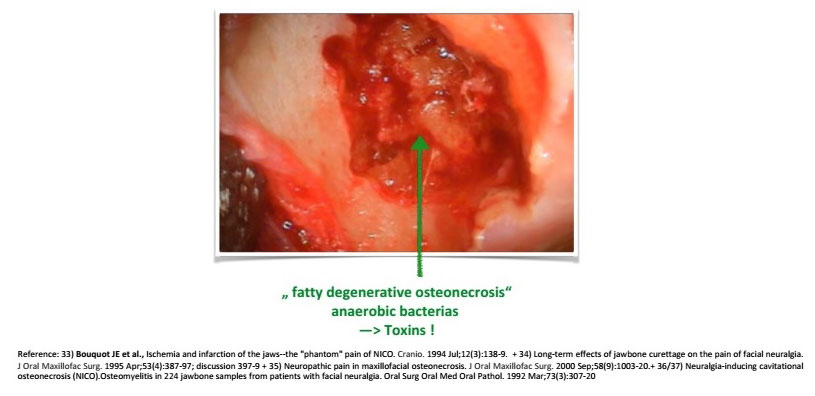
Symptoms
- Locally: Focal inflammation
- painless (33)
- toxine → facial neuralgia/pain (34,35)
- no swelling
- no pus formation
- ischaemic nonresorbing necrotic bone flakes with cavity formation (36)
- microscopic features: dense marrow fibrosis, smudged tissue (37)
Systemically: Action at distance on other organs/organ systems
3. Root canal Treatment (Endodontics)
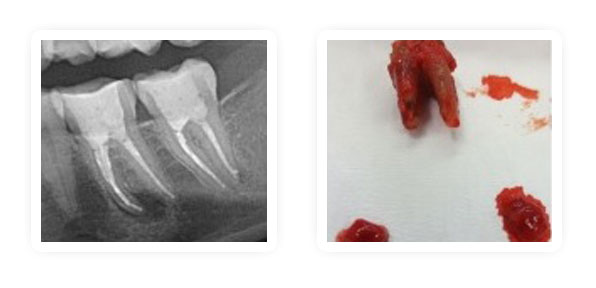
- Oral microorganism/pathogens cause disseminated systemic diseases (38-40)
- Increase in failure rate of endodontic treatments (CAP up to 60%) even with better technical equipment (41-43)
- All improvements and innovations in the field of endodontics have not lead to an improvement in the success rates (44)
- Presence: No changes in the situation, stagnation (45)
Future: Stem cell therapy????

Pathogenesis (46)
Even when the highest standards and the most careful procedures are followed, failures still occur. This is because there are root canal regions that cannot be cleaned and obturated with existing equipments, materials, and techniques, and thus, infection can persist. In very rare cases, there are also factors located within the inflamed periapical tissue that can interfere with post-treatment healing of the lesion. The data on the biological causes
Root canal or canal system?

Leading to........?

Limitations
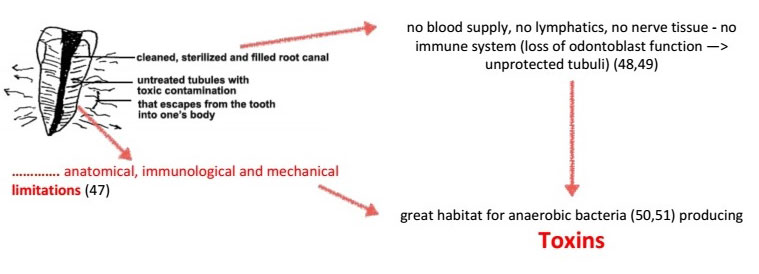

Toxins
Bacterias produce toxic metabolites → carcinogenic hydrogen sulfur compunds (Thioether/Mercaptane → IL-10, INF) (52)
Toxins cause local and systematic diseases by triggering an immune response (53)
Immune Response
Local: adjacent to teeth structures causing cystic lesions, abscesses and jaw cavitations (54-56)
Systemic: Increase in inflammatory markers/cytokines (TNF a, IL 1B, RANTES) circulate through the blood system → chronic inflammation (low pH reduced oxygen saturation/oxidative stress), Cell Proliferation (57-62)

Cell Proliferation
inflammatory markers/cytokines (e.g. TNF alpha, IL 1B, RANTES)
uncontrolled cell proliferation → cancer formation?
Breast, Bladder, Prostate, Cervix (63-69)
! CAVE !
Vital teeth are much more resistant to bacterial invasion than nonvital/root canal treated teeth (70)
The vital pulp plays an important role in the prevention of bacterial invasion and therefore protection!